Home » Session 2: Principles for Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable Agriculture and its Implementation in Hong Kong
Session 2: Principles for Sustainable Agriculture
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, sustainable agriculture “conserves land, water, and plant and animal genetic resources, and is environmentally non-degrading, technically appropriate, economically viable and socially acceptable” (FAO, 1988). It involves the following five interconnected and complementary key principles (FAO, 2014):
20 interconnected actions to guide decision-makers. Technical Reference Document. Rome. 132 pp. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from http://www.fao.org/3/CA1647EN/ca1647en.pdf
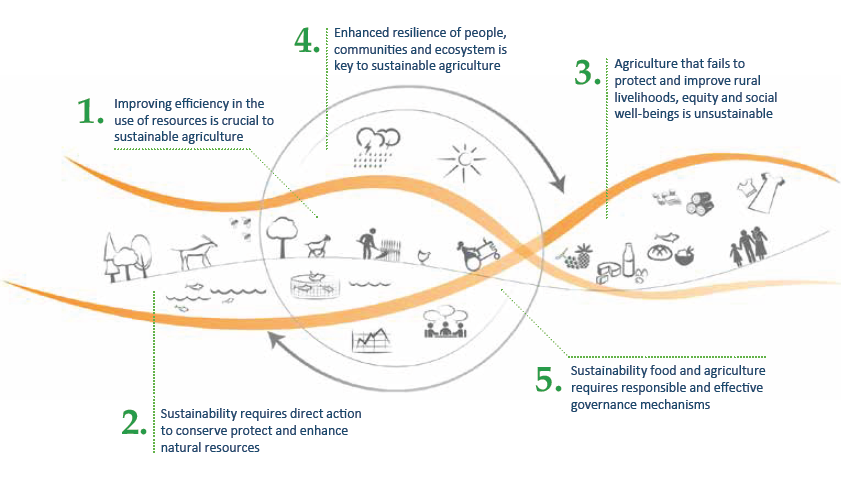
The Five Principles of Sustainable Food and Agriculture
1. Improving Efficiency in the Use of Resources
Agricultural productivity can be increased by modifying current agricultural practices, upgrading the efficiency of existing equipment, and encouraging sustainable use of water and energy. For example, water use efficiency can be increased by replacing flood irrigation with spray or drip irrigation.
2. Conserving, Protecting and Enhancing Natural Resources
Sustainable agriculture seeks to protect and conserve the natural environment, especially soil, air and water. It calls for a drastic change to the common agricultural model which involves intensive use of water, monoculture, chemical fertilisers and pesticides that could lead to serious pollution and ecosystem degradation. Organic farming is friendlier to the ecosystem.
3. Protecting and Improving Rural Livelihoods and Social Well-Being
Rural poverty and food insecurity can be reduced by, for example, improving producers’ access to and control of land and water resources, as well as opening up more channels and building up their capacity for participating in local, regional and international markets.
4. Enhancing Resilience of People, Communities and Ecosystems
Sustainable agriculture calls for policies, technologies and practices that build up rural resilience to agricultural threats such as extreme weather events, market volatility and civil strife. Introduction of pest- or drought- resistant crop varieties is an example of specific measures for enhancing resilience.
5. Promoting Good Governance of Both Natural and Human Systems
A transition to sustainable agriculture requires policy support and favourable legal and institutional environments. Incentive measures have to be in place to encourage farmers to adopt sustainable agricultural practices. Equity, transparency, accountability and the rule of law have to be ensured, and there should be a right balance between public and private initiatives.
These five interconnected principles embrace a range of interdisciplinary agricultural practices. Beyond the notions of betterment of environmental health, economic profitability and social equality, they also link the sustainable food and agriculture system to the 2030 sustainable development goals. Thus, the agriculture field and their stakeholders have a very important role on the implementation of sustainable food and agriculture policies.
Is there any differences between Sustainable Agriculture and Organic Agriculture?"
Continue to “Session 3: Examples of Sustainable Agriculture Practices”
© 2019 Centre for Civil Society and Governance at The University of Hong Kong
Except where otherwise noted, contents of this e-case is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License.
![]()


