Home » Session 2: Principles for Sustainable Food Systems
Sustainable Urban Food Systems and a Collaborative Initiative in Hong Kong
Session 2: Principles for Sustainable Food Systems
The food system of a particular place encompasses the stages from food production, processing, distribution, consumption to disposal, and includes all the interconnected stakeholders involved, the socio-economic and environmental contexts that influence every dimension of the food value chain, as well as the outcomes. A sustainable food system “delivers food security and nutrition for all in such a way that the economic, social and environmental bases to generate food security and nutrition for future generations are not compromised” (HLPE, 2014).
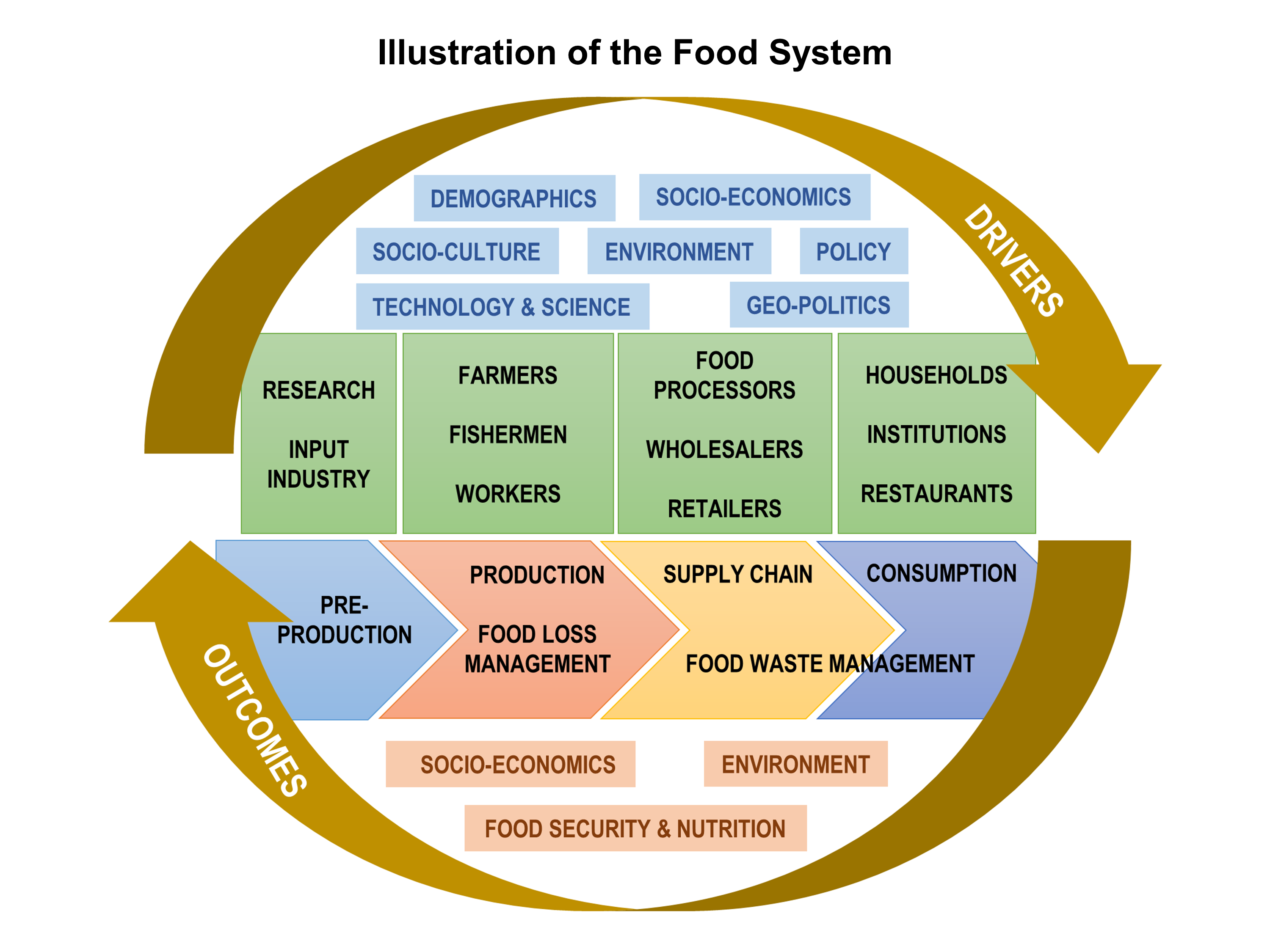
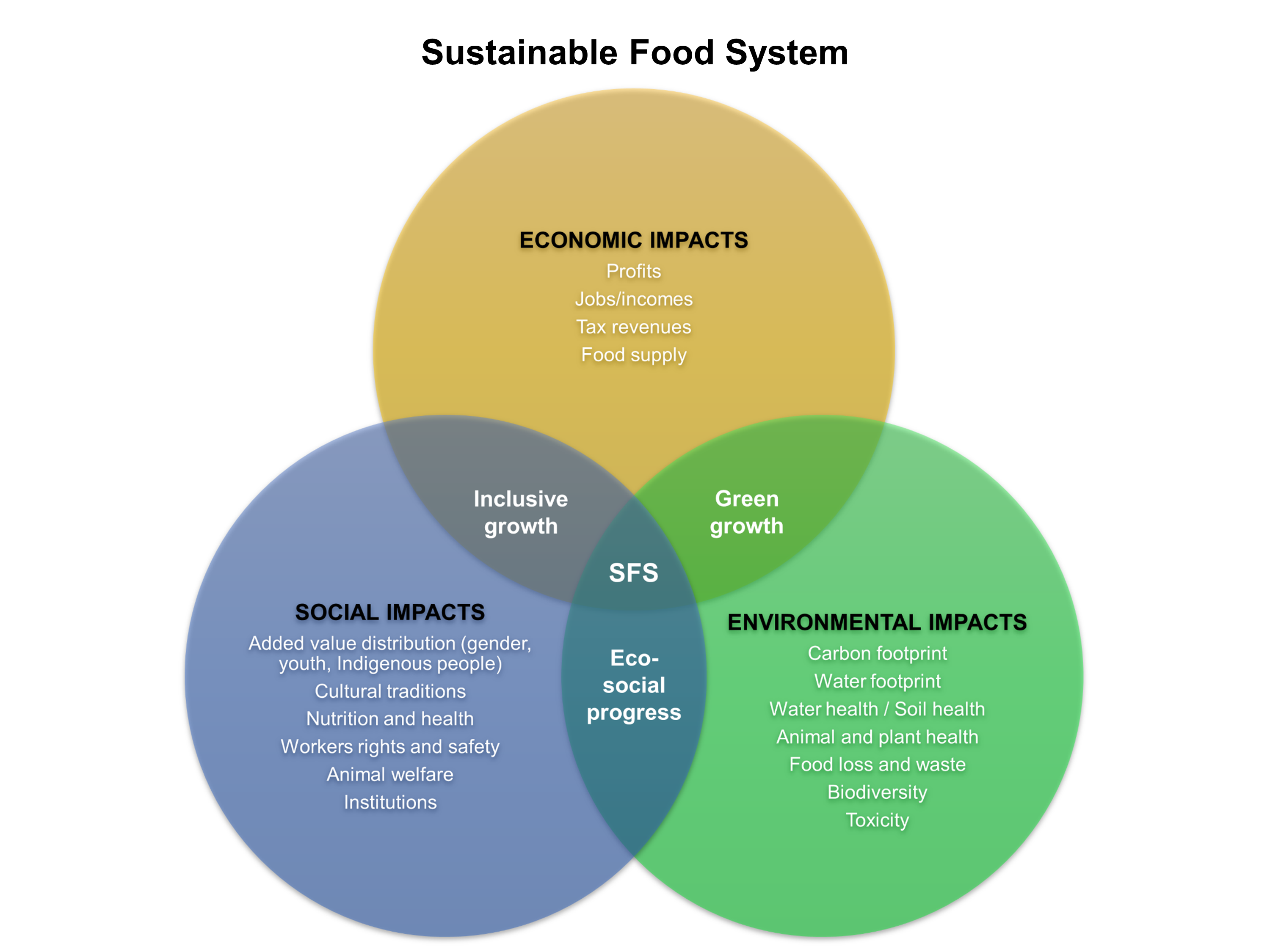
There are five principles for sustainable food systems as identified by the International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems (IPES-Food):
- Sustainable in All Dimensions
Sustainability has to encompass all environmental, health, social, cultural and economic dimensions so as to deliver nourishing, economical and culturally acceptable diets, as well as to ensure long-term food security.
- Diverse & Resilient
The principles of diversity, multi-functionality and resilience should be adopted in food systems in order to ensure sustainability of yields and the agro-ecosystems, as well as diversity in supply chains and markets that supports diverse and nutritious diets.
- Democratic & Empowering
Decision-making in food systems should be inclusive which brings about the empowerment of disadvantaged actors such as small-scaled farmers, disadvantaged consumers etc. and the realisation of human rights of all, including the right to food.
- Socially & Technologically Innovative
Social and technological innovations should take place in the transition to sustainable food systems and play a part in terms of food distribution, retail practices, as well as modes of production.
- Adequately Measured
Existing measures should be supplemented by new indicators of progress so as to assess the sustainability of food systems in terms of their equitability, resilience, diversity and richness in nutrients.
In your daily life, you can support the development of a sustainable food system by adopting sustainable dietary habits. Try to choose nutritious food produced and sold with respect to the ecosystem, the local culture, and the disadvantaged groups. You may pay attention to nutrition labels and sustainable certification labels (for example, the Rainforest Alliance certification helps protect the environment as well as farmers’ livelihoods); help local farmers by buying farm produce from them directly at the farmers’ markets; and also support social enterprises and restaurants that contribute to food system sustainability.
Read more:
FAO. (2014). Sustainable food value chain development – Guiding principles. Rome. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/i3953e/i3953e.pdf
HLPE. (2014). Food losses and waste in the context of sustainable food systems: A report by the High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security. Rome. Retrieved from https://www.fao.org/3/i3901e/i3901e.pdf
International Center for Tropical Agriculture. (2019). Sustainable Food Systems. Retrieved from https://ciat.cgiar.org/about/strategy/sustainable-food-systems/
IPES-Food. (2015). IPES-Food: 10 Principles to guide the transition to Sustainable Food Systems. Retrieved from http://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/IPES%2010%20Principles%20of%20SFS.pdf
Continue to “Session 3: Actions for Building a Sustainable Urban Food System”
© 2019 Centre for Civil Society and Governance at The University of Hong Kong
Except where otherwise noted, contents of this e-case is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License.
![]()


